Adrenaline: Grade 9 Understanding for IGCSE Biology 2.94
Adrenaline is a hormone produced in the adrenal glands which are found on top of the kidneys in the abdomen.
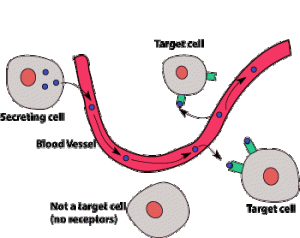
A hormone is “a chemical released by a specialised gland called an endocrine gland into the bloodstream. The hormone travels around the body in the blood plasma and then causes an effect elsewhere in the body by binding to receptors found on certain target cells”.
You should know some other examples of hormones – testosterone, oestrogen, progesterone, ADH – to name a few. Please learn this definition too: it would be wonderful if you got a 3 mark question asking you to define a hormone….
There are many cells in the body that contain receptors for adrenaline. This allows the hormone to exert an effect on a wide variety of tissues. For example there are adrenaline receptors in the pacemaker of the heart and adrenaline will cause the heart to beat faster (more beats per minute) and also with more force.
When is adrenaline released by the adrenal glands into the blood?
Adrenaline is secreted into the blood in times of danger or stress. It prepares the body to either run away from the danger or indeed to battle against it. For this reason, adrenaline is often described as a “fight or flight” hormone.
What are some of the effects of adrenaline?
Target Tissue Effect
Heart Increase in heart rate, increase in cardiac output
Lungs Bronchioles dilate (widen)
Muscles Arteries in muscle dilate to allow more blood to flow to muscles
Skin/Digestive system Arteries in skin/digestive system constrict so less blood flows
Liver Liver breaks down glycogen into glucose to raise blood glucose conc.
Iris Radial muscles in iris contract causing pupil dilation
The overall effect is that the skeletal muscles are supplied with more oxygen and more glucose so they can respire aerobically. This allows the muscle to contract more efficiently.

One comment